Graphs
A graph is a data structure that consists of the following two components:
- A finite set of vertices also called as nodes.
- A finite set of ordered pair of the form (u, v) called as edge.
A binary tree is a graph - limitation it can point to only 2 nodes
Linked List are trees and trees are graphs , meaning linked list is also a graph
Graphs are used to represent many real-life applications: Graphs are used to represent networks. The networks may include paths in a city or telephone network or circuit network. Graphs are also used in social networks like linkedIn, Facebook. For example, in Facebook, each person is represented with a vertex(or node).
The following two are the most commonly used representations of a graph.
Adjacency Matrix
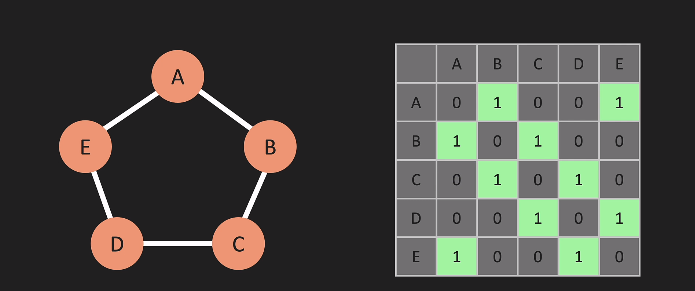
Storing things in Adjacency matrix is not very efficient due to huge number of zeros to be stored when it goes large, hence lets see Adj list:
Adjacency List
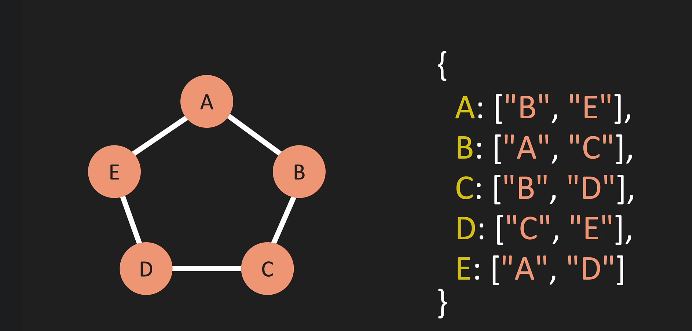
Let's get to code it
class Graph {
constructor() {
this.adjacencyList = {}
}
addVertex(vertex) {
if(!this.adjacencyList[vertex]) {
this.adjacencyList[vertex] = []
return true
}
return false
}
addEdge(vertex1, vertex2) {
if (this.adjacencyList[vertex1] && this.adjacencyList[vertex2]) {
this.adjacencyList[vertex1].push(vertex2)
this.adjacencyList[vertex2].push(vertex1)
return true
}
return false
}
removeEdge(vertex1, vertex2) {
if (this.adjacencyList[vertex1] && this.adjacencyList[vertex2]) {
this.adjacencyList[vertex1] = this.adjacencyList[vertex1]
.filter(v => v !== vertex2)
this.adjacencyList[vertex2] = this.adjacencyList[vertex2]
.filter(v => v !== vertex1)
return true
}
return false
}
removeVertex(vertex) {
if (!this.adjacencyList[vertex]) return undefined
while(this.adjacencyList[vertex].length) {
let temp = this.adjacencyList[vertex].pop()
this.removeEdge(vertex, temp)
}
delete this.adjacencyList[vertex]
return this
}
}
let myGraph = new Graph()
myGraph.addVertex("A")
myGraph.addVertex("B")
myGraph.addVertex("C")
myGraph.addVertex("D")
myGraph.addEdge("A", "B")
myGraph.addEdge("A", "C")
myGraph.addEdge("A", "D")
myGraph.addEdge("B", "D")
myGraph.addEdge("C", "D")