WhyThis
Why need for DSA?
If you are reading this, than you already know the why we need it. We are discussing a few topics here, connect with me if you want to know more
Linked List
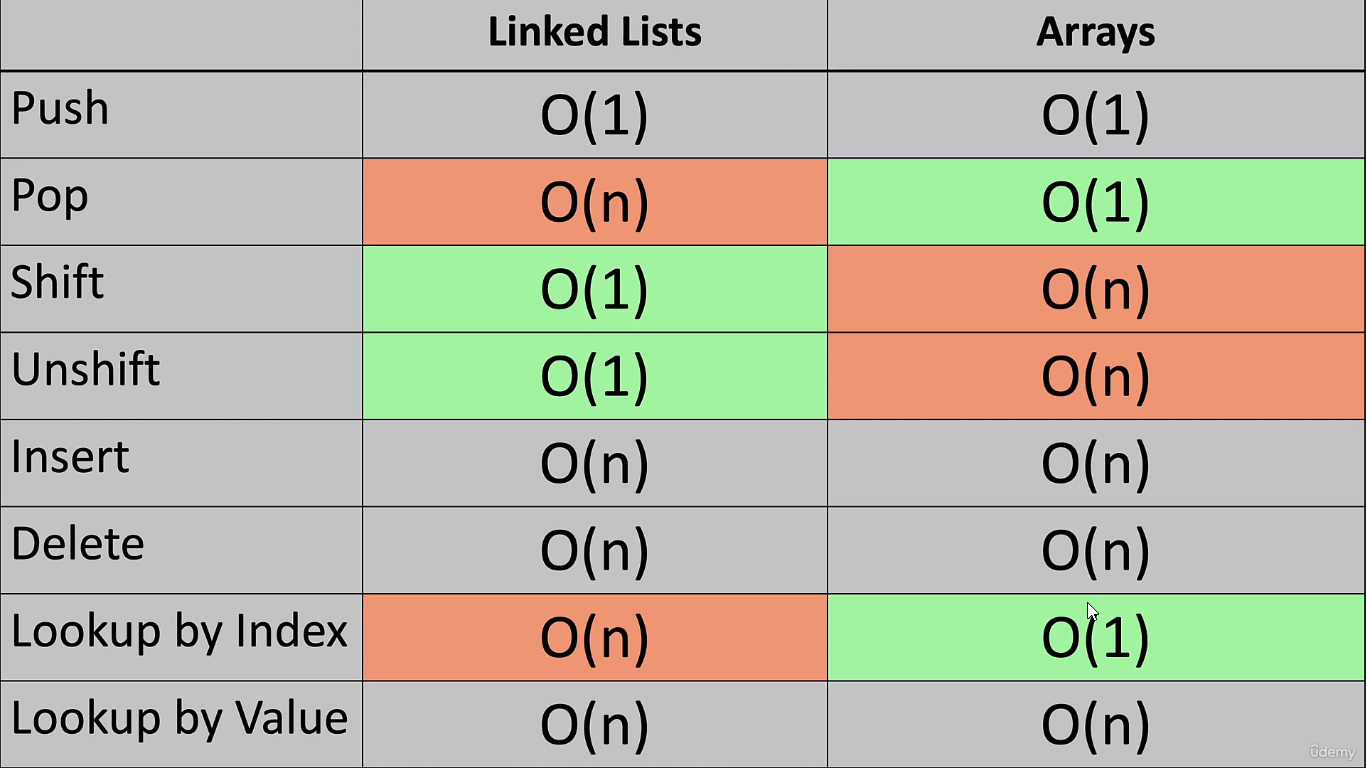
Its different from Array in terms of performance
- No indexes
- can store any type of data
- shift and unshift takes only n(1)
Linked lists are often used because of their efficient insertion and deletion. They can be used to implement stacks, queues, and other abstract data types.
As per GFG
LinkedList is the dynamic data structure, as we can add or remove elements at ease, and it can even grow as needed. Just like arrays, linked lists store elements sequentially, but don't store the elements contiguously like an array
//create a node
// A linkedList is a collection of objects which has a head and tail pointing to next objects
// It's different from Array in terms of performance
//1. No indexes
//2. can store any type of data
//3. shift and unshift takes only
// Pseudoscope
// 1. Check whether node exists
// 2. If not create one
// 3. Point LL's head and tail both to that node
// 4. Implement push method
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor(value) {
const newNode = new Node(value)
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = this.head;
this.length = 1;
}
push(value) {
const newNodePoint = new Node(value);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNodePoint;
this.tail = newNodePoint;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNodePoint;
this.tail = newNodePoint;
}
this.length++;
return this;
}
//for popping out we need to keep track of
// 1. last item
// 2. Second last item - so that tail could be pointed to that
pop() {
// if no length, return undefined
if (!this.length)
return undefined;
//if length 1 , set head, tail , pre , post to null
//if length>1 then have two pointers
let pre = this.head;
let curr = this.head;
while (curr.next) {
pre = curr;
curr = curr.next;
}
this.tail = pre;
this.tail.next = null;
this.length--;
if (this.length === 0) {
this.head = null
this.tail = null
}
return curr;
}
//need to create a new node and then point node's next value to header
//will need a temp variable to point to curr node so that header can be pointed to it
unshift(value) {
let newNodePt = new Node(value);
//either use push method if node doesnt exists
if (!this.head)
return this.push(value)
//or you can create node and point head and tail at them
// this.head = this.tail = newNodePt
newNodePt.next = this.head;
this.head = newNodePt;
this.length++
}
shift() {
if (!this.head)
return undefined;
var temp = this.head;
this.head = this.head.next;
temp.next = null;
this.length--;
if (this.length === 0) {
this.tail = null
}
}
get(index) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.length)
return undefined;
let curr = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
curr = curr.next
}
return curr;
}
set(value, index) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.length)
return undefined;
let temp = this.get(index);
if (temp) {
temp.value = value
return true
}
return false
}
insert(index, value) {
//insert from rightmost
if (index === this.length) {
return this.push(value);
}
//insert from leftmost
if (index === 0) {
return this.unshift(value);
}
if (index < 0 || index > this.length)
return undefined;
//insert at given index
let curr = this.get(index - 1);
const newNodePt = new Node(value);
newNodePt.next = curr.next;
curr.next = newNodePt;
this.length++;
return true;
}
remove(index) {
//if length is 0, return undefined
if (this.length === 0)
return undefined;
if (this.length === 1 && index === 1) {
this.tail = this.head = null;
return true
}
if (index === 0)
return this.shift();
if (index === this.length - 1)
return this.pop();
if (index < 0 || index > this.length)
return undefined;
const prev = this.get(index - 1)
const temp = prev.next;
prev.next = temp.next;
temp.next = null;
this.length--;
return temp;
}
//damn tricky - try writing by yourself
reverse() {
if (this.length === 0 || this.length === 1) {
return this;
}
const tempvar = this.head
this.head = this.tail;
this.tail = tempvar;
let temp = this.tail
let prev = null;
let next = null;
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
next = temp.next;
temp.next = prev;
prev = temp;
temp = next;
}
return this;
}
}
const a = new LinkedList(1);
a.push(2)
a.push(3)
a.unshift(11)
a.unshift(12)
console.log(a);